In HTML5 and EPUB3 digital files, several textual components are associated with a visual resource and can be used together to effectively describe it. It is important to note that different elements are available to different users. The relationships among the elements and the definitions of them are explained below.
Definitions
- Alt text
- shorter text (often 140 characters or fewer) associated with a specific visual resource, accessed via assistive technology; shorthand for “alternative text”
- Assistive technology
- any technology or device that enhances the capacities of its user (often a user with disabilities); in the context of reading, usually screen readers, text to speech, literacy software, speech recognition, voice command, and adaptive input
- Body
- the main text of the publication, available via all reading technology
- Caption
- shorter text associated with a specific visual resource, or a group of visual resources presented together, available via all reading technology
- Description
- any text that describes the visual resource in a manner that translates into words its content or purpose in the publication; in other contexts including museum education and multimedia accessibility, description may be called “audio description,” “verbal description,” or “visual description”
- EPUB
- electronic publication format based on HTML, standards for which are maintained by the International Digital Publishing Forum
- HTML
- abbreviation for HyperText Markup Language; machine-readable format consisting of text and markup used to create documents on the world wide web
- Machine reader
- technology that “reads” digital publications to search and index, display, or convert text to speech
- Long description
- longer text associated with a specific visual resource, accessed via assistive technology; may contain structural elements or subsections (e.g. a table, paragraphs)
- Reading technology
- any technology that interacts with a digital publication to present it to a reader
- Visual resource
- the electronic image file included in a publication, or the original visual work it represents
Relationships
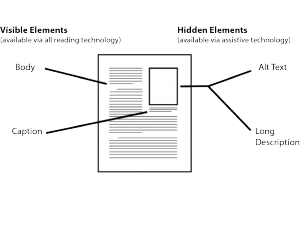
Visible text elements
available to readers using all common reading technology
- Body
- Caption
Hidden text elements
available only to readers using assistive technology and machine readers
- Alt text
- Long description
Notes
Assistive technology: Technologies will change. The history of technology shows that what is “assistive” often becomes “mainstream.” Although alt text and long description are currently available only via assistive technology, future reading technology may present them to more users for more purposes.
Alt text: In HTML environments, i.e. web browsers, alt text is available without assistive technologies in certain cases: most commonly, when an image fails to load.
Interoperability: Interoperability will change. Although the text associated with a visual resource (caption, alt text, long description) must currently be written into each individual publication, future publishing technology may allow such text to be retrieved from image metadata databases or other sources.
Guidelines Contents